Saudi Arabia sanctions under Mohammed bin Salman reveal a strategic use of economic pressure, targeting countries like Qatar, Turkey, and Lebanon, while controversially avoiding action against Israel-linked interests.
Saudi Arabia’s approach to economic sanctions has come under renewed scrutiny, with critics pointing out what they see as a selective and politically motivated strategy. From the blockade of Qatar to the embargoes on Lebanon and Turkey, the Saudi Arabia sanctions policy is increasingly being viewed as a tool used by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman to advance specific geopolitical interests, while turning a blind eye to others.
According to a report by the Saudi opposition newspaper Voice of the People, the crown prince’s pattern of putting and withholding sanctions is raising questions about the consistency and motivations behind Saudi Arabia’s foreign policy.
A Pattern of Political Sanctions
Sanctions Against Qatar
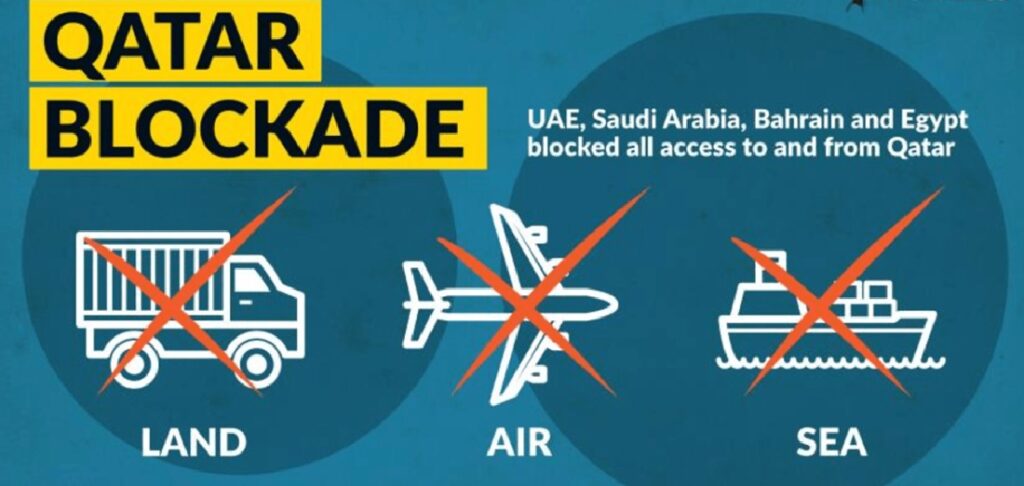
Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, and Egypt simultaneously severed their bilateral relations with Qatar and banned Qatari aircraft and ships from utilizing their sovereign territory by air, land, and sea
In June 2017, Saudi Arabia launched a comprehensive blockade against Qatar, severing all diplomatic ties and shutting down land, sea, and air routes. The sanctions were part of a broader effort, supported by the UAE, Bahrain, and Egypt to isolate Doha over alleged ties to terrorism and its relations with Iran.
The campaign included media offensives and public calls for boycotts. Saudi media was reportedly mobilized to exacerbate the crisis for Qataris, amplifying the impact of the blockade on the country’s economy and social structure.
Saudi Arabia Sanctions Against Turkey
In 2020, relations between Riyadh and Ankara soured further, particularly over differing positions on Qatar and the assassination of Saudi journalist Jamal Khashoggi in Istanbul in 2018.
Saudi Arabia responded by enforcing unofficial sanctions against Turkey. These measures targeted not only goods but also Saudi investments in Turkish businesses, leading to significant financial losses. Trade between the two countries dropped dramatically as Mohammed bin Salman pushed for a complete freeze on exports, imports, and other commercial exchanges.
Lebanon Becomes Another Target
Following the devastating Beirut port explosion in August 2020, Lebanon entered a deeper financial and political crisis. Instead of offering support, Saudi Arabia imposed a series of strict sanctions, cutting off financial aid and halting all trade activities.
The Saudi Arabia sanctions on Lebanon were seen by many analysts as part of a broader attempt to weaken Hezbollah’s influence in the region. However, the move significantly worsened Lebanon’s economic collapse and strained its already fragile infrastructure.
Contradictory Stance on Israel Sparks Controversy
No Sanctions, Active Promotion of Israeli-linked Brands
Despite Saudi Arabia’s active use of sanctions against neighboring Muslim nations, the kingdom has adopted a markedly different stance when it comes to Israel. During Israel’s recent military operation in Gaza, which resulted in widespread civilian casualties, many Arab and Muslim nations called for a boycott of Israeli products.
Saudi Arabia, however, not only refrained from participating in such efforts but reportedly promoted Israeli-linked businesses within its borders.
McDonald’s Advertising During Gaza War
One of the most prominent examples of this perceived contradiction was the kingdom’s public promotion of McDonald’s during the war in Gaza. Social media users circulated a now-deleted video of Turki Al-Sheikh, head of Saudi Arabia’s General Entertainment Authority, encouraging Saudis to visit McDonald’s during the “Riyadh Season” festival.
In the video, Al-Sheikh described McDonald’s as the official partner of the event, even offering a buy-one-get-one-free meal deal. The promotion drew heavy criticism online, especially after footage emerged showing McDonald’s franchises in Israel distributing free meals to Israeli soldiers.
Public Backlash and Deleted Evidence
Social Media Uproar
The campaign sparked outrage across the Arab world. Activists accused the Saudi government of hypocrisy, pointing out the disparity between its treatment of regional Muslim countries and its silence on Israeli military actions.
Although the video by Al-Sheikh was later removed, a tweet with similar messaging remained on his official account, further fueling public anger. McDonald’s quickly became one of the primary targets of boycott campaigns across Arab nations.
Conclusion: Sanctions as a Political Weapon
Saudi Arabia’s current sanctions strategy appears to prioritize political alignment over humanitarian or ethical considerations. From enforcing embargoes against Turkey, Lebanon, and Qatar, to promoting corporations linked with Israel during a time of conflict, the Saudi Arabia sanctions model is increasingly being criticized as inconsistent and self-serving.
As the kingdom continues to assert its influence across the Middle East, observers argue that transparency and consistency in foreign policy will be critical if Saudi Arabia wants to be seen as a legitimate regional power rather than a geopolitical opportunist.




